From Keywords to Conversations
How LLMs Are Rewriting the Rules of SEO
The End of Keyword-First SEO
Since Google was founded, they’ve shaped the way in which we’ve searched. In order to provide you with the best result, they’ve conditioned us to search for short 1-3 keyword phrases to best match intent. But that’s not really how we’re used to asking for information and it often missed the nuance of what I was really trying to search for. This inevitably meant having to spend more and more time refining my searches to try and work out what keywords Google wanted me to search for, rather than the way I would search.
As a result, it also meant that search, and SEO, was fairly mathematical. By ensuring your target keyword was stuffed onto the page in the right places was often enough to trigger high rankings. But that’s not how it works anymore.
AI tools like ChatGPT and Google’s AI Overviews and AI Mode now answer questions directly, often without users clicking a single link. Search isn’t just keywords anymore, it’s becoming more conversational.
How LLMs Understand Intent
Large language models (LLMs) don’t need to rely on keywords in the same way that Google and other search engines used to. They interpret meaning, and most importantly, understand context.
Using embeddings and probabilistic reasoning, LLMs map the relationships between different topics and entities to understand meaning and context. For example, I was recently looking for a new second-hand car and went to ChatGPT to help me narrow down my search (I know next to nothing about what to look out for in a used car). When I searched for ‘best mid-sized compact SUV that’s good for families, but not too big and has plenty of boot space” chatGPT was able to understand that the model of car, the size, and its utility (good for families in this case means spacious, safe, can fit car seats/buggies etc) all play a part in the search. It’s able to go beyond the obvious search query and provide greater context and intent. The result was a solid list of makes and models that hit each of the criteria in one nicely summarised table.
From Keywords to Conversations
As a result, we’re starting to see a shift in search behaviour as more and more people use LLMs for search. People aren’t just searching anymore, they’re having a conversation. They ask questions, refine, clarify, and keep going, allowing them to gather a huge amount of information much more efficiently than through traditional search.
ChatGPT, and AI Mode have turned queries into ongoing dialogues, and when search becomes conversational, SEO will have to change too. It’s no longer just about ranking for the first query, it’s about staying relevant across that entire conversation. And that’s the biggest opportunity (or challenge!).
The Fall of Keywords, the Rise of Semantic Clusters
As keywords become less relevant, and the importance of context grows, there’s a lot of discussion around ‘semantic clusters’: groups of related topics and content that collectively signal depth and authority.
Whilst this all sounds new and fancy in the age of AI, it’s essentially what content SEO has been talking about for years. Content hubs. Hub and spoke, pillar content, and supporting content, whatever you want to call it, it all does the same thing, helping crawlers get a better understanding of your topical relevance.
Both Google and ChatGPT are looking for the same thing and you need to be building out a body of work that proves you deeply understand, and are an authority on the subject.
Writing for Natural Language
With conversation becoming more normal, so does the language we use when we search. This means targeting more natural, question-based structures (who, how, why, what, if) and building supporting articles that anticipate what a user might ask next. When looking at the types of queries that people are searching for that trigger AIOs for example, across our data set, we see roughly ⅓ of all keywords are question based.
Structured data, like FAQ, or how-to schema can also further help provide context, but ultimately it comes down to clarity. LLMs like simple easy to grab information, and the clearer this is laid out the better.
How Search Results Are Changing
We can already see the impact of this with Google’s AIOs and AI Mode
AI Overviews sit right at the top of the SERP, pushing traditional organic listings further down the page and providing multiple cited sources from where they draw their data. ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude similarly now serve as their own “search layers,” pulling from multiple sources to create citation-based answers.
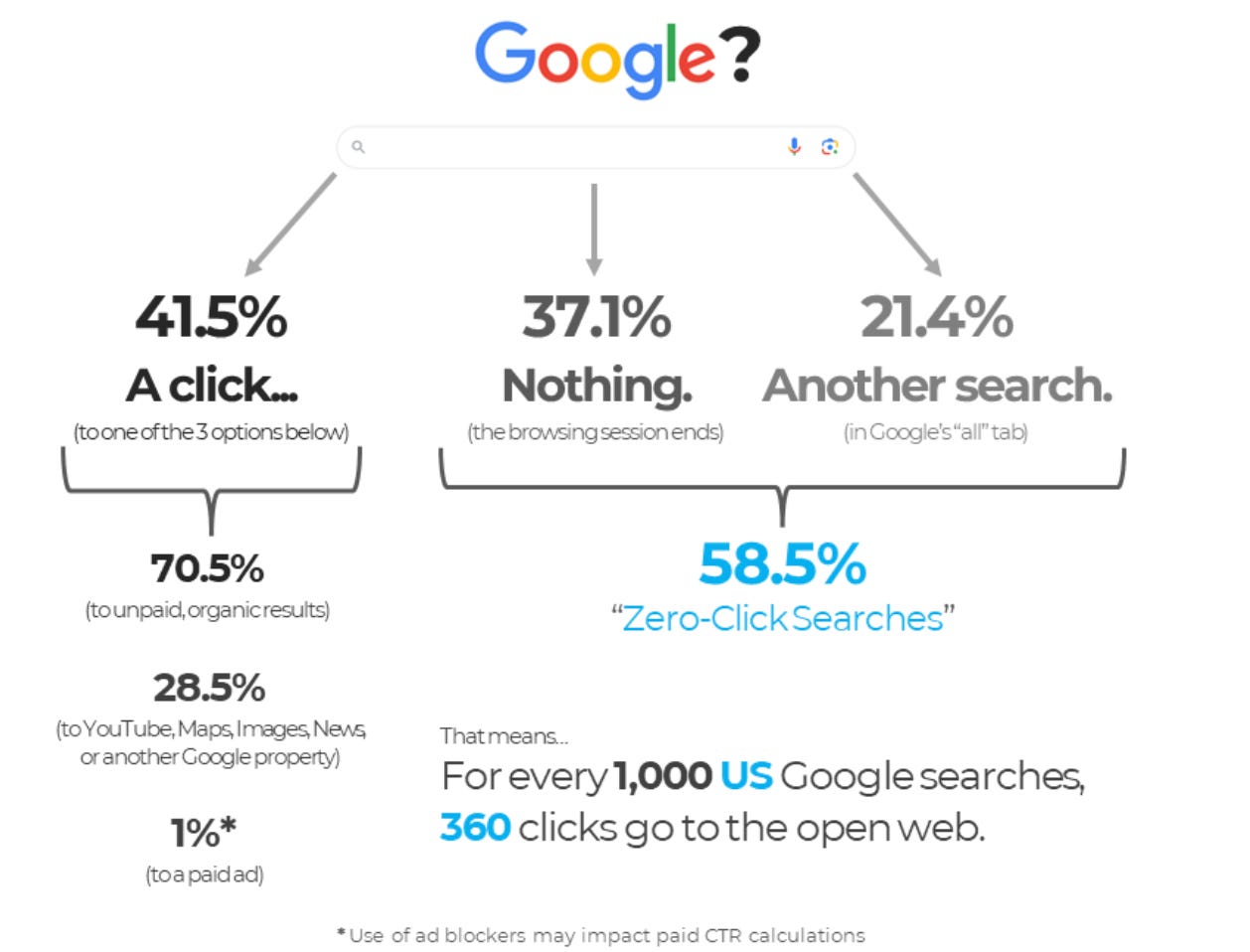
As a result, zero click searches are on the rise, and clicks aren’t the reliable metric for success as they used to be. Brand visibility and share of voice are now more and more relevant. Are you being quoted or referenced by the LLMs generating these summaries? That’s now what really counts
The New SEO Playbook
SEO always adapts, and after years of stagnation, there is a new area to play with conversation optimisation.
It now means mapping intent, entities, and semantic clusters, ultimately understanding not just what people are asking for now, but what they might ask next. This also means publishing content in multiple formats, from blog posts to snippets to data tables, that AI models can pull from, and it means focusing on signals that matter to both readers and algorithms EEAT (expertise, experience, authority, and trust)
From Search to Understanding
Search has always been about finding information. Now it’s also about understanding it.
LLMs have ultimately made search more human, and that means SEO needs to follow suit. The future of SEOs won’t just be chasing algorithm updates, it’ll be studying conversations, behaviour, and trust, as being understood will become more valuable than simply just being found.
Ed Coles, Head of SEO, KAIZEN
___
Fancy a free brand audit? Book a short intro call!